Benefits of Beets (Red Root)
Health Benefits:
Help Fight Inflammation:
Chronic inflammation is associated with a number of diseases, such as obesity, heart disease, liver disease and cancer.
Beets contain pigments called betalains, which may potentially possess a number of anti-inflammatory properties.
However, most of the research in this area has been conducted in rats.
Beetroot juice and beetroot extract have been shown to reduce kidney inflammation in rats injected with toxic chemicals known to induce serious injury.
One study in humans with osteoarthritis showed that betalain capsules made with beetroot extract reduced pain and discomfort associated with the condition.
While these studies suggest that beets have an anti-inflammatory effect, human studies are needed to determine whether beets could be used to reduce inflammation.
Chronic inflammation is associated with a number of diseases, such as obesity, heart disease, liver disease and cancer.
Beets contain pigments called betalains, which may potentially possess a number of anti-inflammatory properties.
However, most of the research in this area has been conducted in rats.
Beetroot juice and beetroot extract have been shown to reduce kidney inflammation in rats injected with toxic chemicals known to induce serious injury.
One study in humans with osteoarthritis showed that betalain capsules made with beetroot extract reduced pain and discomfort associated with the condition.
While these studies suggest that beets have an anti-inflammatory effect, human studies are needed to determine whether beets could be used to reduce inflammation.
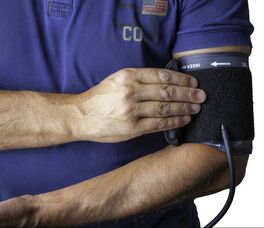
Help Keep Blood Pressure in Check:
Heart disease, including heart attacks, heart failure and stroke, is one of the leading causes of death worldwide.
And high blood pressure is one of the leading risk factors for the development of these conditions.
Studies have shown that beets can significantly lower blood pressure by up to 4–10 mmHg over a period of only a few hours.
The effect appears to be greater for systolic blood pressure, or pressure when your heart contracts, rather than diastolic blood pressure, or pressure when your heart is relaxed. The effect may also be stronger for raw beets than cooked beets .
These blood pressure-lowering effects are likely due to the high concentration of nitrates in beets. In your body, dietary nitrates are converted into nitric oxide, a molecule that dilates blood vessels, causing blood pressure to drop.
Blood nitrate levels remain elevated for about six hours after eating dietary nitrate. Therefore, beets only have a temporary effect on blood pressure, and regular consumption is required to experience long-term reductions in blood pressure.
Heart disease, including heart attacks, heart failure and stroke, is one of the leading causes of death worldwide.
And high blood pressure is one of the leading risk factors for the development of these conditions.
Studies have shown that beets can significantly lower blood pressure by up to 4–10 mmHg over a period of only a few hours.
The effect appears to be greater for systolic blood pressure, or pressure when your heart contracts, rather than diastolic blood pressure, or pressure when your heart is relaxed. The effect may also be stronger for raw beets than cooked beets .
These blood pressure-lowering effects are likely due to the high concentration of nitrates in beets. In your body, dietary nitrates are converted into nitric oxide, a molecule that dilates blood vessels, causing blood pressure to drop.
Blood nitrate levels remain elevated for about six hours after eating dietary nitrate. Therefore, beets only have a temporary effect on blood pressure, and regular consumption is required to experience long-term reductions in blood pressure.

Boost Digestion:
Dietary fiber is an important component of a healthy diet.
It has been linked to many health benefits, including improved digestion.
One cup of beetroot contains 3.4 grams of fiber, making beets a good fiber source.
Fiber bypasses digestion and heads down to the colon, where it either feeds the friendly gut bacteria or adds bulk to stool.
This can promote digestive health, keep you regular and prevent digestive conditions like constipation, inflammatory bowel disease and diverticulitis.
Moreover, fiber has been linked to a reduced risk of chronic diseases including colon cancer, heart disease and type 2 diabetes.
Dietary fiber is an important component of a healthy diet.
It has been linked to many health benefits, including improved digestion.
One cup of beetroot contains 3.4 grams of fiber, making beets a good fiber source.
Fiber bypasses digestion and heads down to the colon, where it either feeds the friendly gut bacteria or adds bulk to stool.
This can promote digestive health, keep you regular and prevent digestive conditions like constipation, inflammatory bowel disease and diverticulitis.
Moreover, fiber has been linked to a reduced risk of chronic diseases including colon cancer, heart disease and type 2 diabetes.
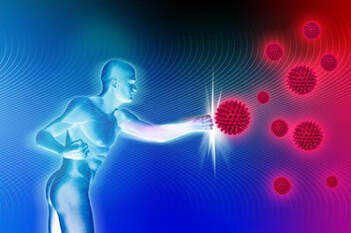
Boost Immunity:
Beets are extremely nutrient dense which helps boost immunity levels in the body and it is known to fight fever and colds. Vitamin C, B-complex, and powerful antioxidants in these root vegetables help prevent fatigue, soothe minor aches and pains, and reduce inflammation.
Beets are extremely nutrient dense which helps boost immunity levels in the body and it is known to fight fever and colds. Vitamin C, B-complex, and powerful antioxidants in these root vegetables help prevent fatigue, soothe minor aches and pains, and reduce inflammation.
Brain Health:
Beets improves brain neuroplasticity due to the nitrates present in them. These nitrates help increase oxygenation of the somatomotor cortex, a brain area that is often affected in the early stages of dementia. As people get older, blood flow to the brain decreases, which often leads to decreased cognition. Eating beets can slow or prevent this process. The study published in the Journals of Gerontology confirms that beetroot juice in combination with exercise in older adults can have a more positive impact.
Beets improves brain neuroplasticity due to the nitrates present in them. These nitrates help increase oxygenation of the somatomotor cortex, a brain area that is often affected in the early stages of dementia. As people get older, blood flow to the brain decreases, which often leads to decreased cognition. Eating beets can slow or prevent this process. The study published in the Journals of Gerontology confirms that beetroot juice in combination with exercise in older adults can have a more positive impact.

Promote Weight Loss:
Packed with nutrients and fiber, beets are an excellent addition to a weight-loss diet. Magnesium and potassium in beets help to detoxify the body and flush out excess water, preventing bloating. These nutrients help to optimize metabolism and losing excess weight. Beet juice is often prescribed in detoxifying diets.
Packed with nutrients and fiber, beets are an excellent addition to a weight-loss diet. Magnesium and potassium in beets help to detoxify the body and flush out excess water, preventing bloating. These nutrients help to optimize metabolism and losing excess weight. Beet juice is often prescribed in detoxifying diets.
Anticancer Potential:
A study by Dr. Govind J.Kapadia of Howard University in the United States has revealed that beets may be good at preventing skin, lung, and colon cancer. They contain the pigment betacyanins, which counteracts cancerous cell growth. Nitrates used in meats as preservatives can stimulate the production of nitrosamine compounds in the body, which can also result in cancer. Recent studies have shown that beet juice inhibits the cell mutations caused by these compounds. Also, the natural beta-carotene in beetroot may help to prevent lung cancer.
A study by Dr. Govind J.Kapadia of Howard University in the United States has revealed that beets may be good at preventing skin, lung, and colon cancer. They contain the pigment betacyanins, which counteracts cancerous cell growth. Nitrates used in meats as preservatives can stimulate the production of nitrosamine compounds in the body, which can also result in cancer. Recent studies have shown that beet juice inhibits the cell mutations caused by these compounds. Also, the natural beta-carotene in beetroot may help to prevent lung cancer.
Promote Liver Detoxification:
Betaines, in beets, stimulate the functions of the liver and keep it healthy, according to one animal study. Also, pectin, a water-soluble fiber in these root vegetables, helps flush out toxins from the liver. They are one of the superfoods that have the ability to reverse fatty liver.
Betaines, in beets, stimulate the functions of the liver and keep it healthy, according to one animal study. Also, pectin, a water-soluble fiber in these root vegetables, helps flush out toxins from the liver. They are one of the superfoods that have the ability to reverse fatty liver.

Improve Heart Health:
Betaine, present in beets, is a powerful bioactive compound that helps lower the levels of homocysteine in the body. High levels of homocysteine can cause cardiovascular problems, such as heart attacks, and strokes. Betalains further help inhibit chronic inflammation when it comes to heart disease.
The fiber in beets helps reduce cholesterol and triglycerides by increasing the level of good HDL cholesterol. The fiber also works to eliminate excess LDL (bad) cholesterol from the body quickly. Thus, consumption of beets helps prevent cardiovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis in multiple ways, as per a study published in the journal Nutrients.
Betaine, present in beets, is a powerful bioactive compound that helps lower the levels of homocysteine in the body. High levels of homocysteine can cause cardiovascular problems, such as heart attacks, and strokes. Betalains further help inhibit chronic inflammation when it comes to heart disease.
The fiber in beets helps reduce cholesterol and triglycerides by increasing the level of good HDL cholesterol. The fiber also works to eliminate excess LDL (bad) cholesterol from the body quickly. Thus, consumption of beets helps prevent cardiovascular diseases such as atherosclerosis in multiple ways, as per a study published in the journal Nutrients.
Increased Energy Levels:
Beets contain a significant amount of carbohydrates that provide energy for prolonged sports activities. Carbohydrates are the natural building blocks of energy metabolism, and beets provide them without any of the negative side effects of many other carbohydrate-heavy foods. Optimal levels of carbs ensure the peak functioning of all important metabolic reactions that keep the organs functioning efficiently.
Beets contain a significant amount of carbohydrates that provide energy for prolonged sports activities. Carbohydrates are the natural building blocks of energy metabolism, and beets provide them without any of the negative side effects of many other carbohydrate-heavy foods. Optimal levels of carbs ensure the peak functioning of all important metabolic reactions that keep the organs functioning efficiently.
Nutrition Facts:
Beets mainly consist of water (87%), carbs (8%), and fiber (2–3%).
One cup (136 grams) of boiled beetroot contains fewer than 60 calories, while 3/4 cup (100 grams) of raw beets boasts the following nutrients:
One cup (136 grams) of boiled beetroot contains fewer than 60 calories, while 3/4 cup (100 grams) of raw beets boasts the following nutrients:
- Calories: 43
- Water: 88%
- Protein: 1.6 grams
- Carbs: 9.6 grams
- Sugar: 6.8 grams
- Fiber: 2.8 grams
- Fat: 0.2 grams
Carbs:
Raw or cooked beetroot offers about 8–10% carbs.
Simple sugars — such as glucose and fructose — make up 70% and 80% of the carbs in raw and cooked beetroots, respectively.
Beetroots are also a source of fructans — short-chain carbs classified as FODMAPs. Some people cannot digest FODMAPs, causing unpleasant digestive symptoms.
Beetroots have a glycemic index (GI) score of 61, which is considered medium. The GI is a measure of how fast blood sugar levels rise after a meal .
On the other hand, the glycemic load of beetroots is only 5, which is very low.
This means that beetroots should not have a major effect on blood sugar levels because the total carb amount in each serving is low.
Raw or cooked beetroot offers about 8–10% carbs.
Simple sugars — such as glucose and fructose — make up 70% and 80% of the carbs in raw and cooked beetroots, respectively.
Beetroots are also a source of fructans — short-chain carbs classified as FODMAPs. Some people cannot digest FODMAPs, causing unpleasant digestive symptoms.
Beetroots have a glycemic index (GI) score of 61, which is considered medium. The GI is a measure of how fast blood sugar levels rise after a meal .
On the other hand, the glycemic load of beetroots is only 5, which is very low.
This means that beetroots should not have a major effect on blood sugar levels because the total carb amount in each serving is low.
Fiber:
Beetroots are high in fiber, providing about 2–3 grams in each 3/4-cup (100-gram) raw serving.
Dietary fiber is important as part of a healthy diet and linked to a reduced risk of various diseases.
Beetroots are high in fiber, providing about 2–3 grams in each 3/4-cup (100-gram) raw serving.
Dietary fiber is important as part of a healthy diet and linked to a reduced risk of various diseases.

Vitamins and Minerals:
Beetroots are a great source of many essential vitamins and minerals.
Beetroots are a great source of many essential vitamins and minerals.
- Folate (vitamin B9). One of the B vitamins, folate is important for normal tissue growth and cell function. It’s particularly necessary for pregnant women.
- Manganese. An essential trace element, manganese is found in high amounts in whole grains, legumes, fruits, and vegetables.
- Potassium. A diet high in potassium can lead to reduced blood pressure levels and positive effects on heart health .
- Iron. An essential mineral, iron has many important functions in your body. It’s necessary for the transport of oxygen in red blood cells.
- Vitamin C. This well-known vitamin is an antioxidant that is important for immune function and skin health.
Other Plant Compounds:
Plant compounds are natural plant substances, some of which may aid health.
The main plant compounds in beetroots are:
Plant compounds are natural plant substances, some of which may aid health.
The main plant compounds in beetroots are:
- Betanin. Also called beetroot red, betanin is the most common pigment in beetroots, responsible for their strong red color. It is believed to have various health benefits.
- Inorganic nitrate. Found in generous amounts in leafy green vegetables, beetroots, and beetroot juice, inorganic nitrate turns into nitric oxide in your body and has many important functions .
- Vulgaxanthin. A yellow or orange pigment found in beetroots and yellow beets.
How to Eat?
Beets can be eaten in many ways but before consuming them, one needs to remove the thin skin. Here are some of the ways you can use beets in your daily diet:
- Salads and soups: Beets can be sliced and added to a salad, or they can also be simply eaten raw. Remove its thin skin, slice, and season the beet with salt, pepper, and lemon juice, and a healthy snack is ready. Another way to eat them is by using them to make soups, like the traditional Borscht.
- Roasted or steamed beets: You can roast beets whole or sliced. You can also add them to your roasted root vegetable mix. The other way to cook beets is to steam them. Quarter the unpeeled beets and steam them for 15 minutes.

- Pickled beets: You can easily make pickled beets at home by using vinegar, and they are also available in grocery stores. Pickled beets are low in fat and are a rich source of dietary fiber, carbohydrates, and minerals.

- Beet juice: You can easily make beet juice by putting them in a blender.

- Desserts: Beets are used commonly in vegan chocolate cakes as they pair well with chocolate and help give these plant-based dishes a deeper flavor.
- Beet greens: The greens are used to make a side dish or in salads. These leaves are packed with important nutrients such as potassium, copper, magnesium, and vitamin A, K, and C. They also help lower your risk of chronic diseases such as type-2 diabetes and stroke.
Recipes:
Healthy recipes: http://www.eatingwell.com/recipes/19290/ingredients/vegetables/beets/
Raw Vegan recipes: http://rawfoodrecipes.com/ingredient/beet/
Beet soups: https://www.allrecipes.com/recipe/89057/beet-soup/
21 beet dessert recipes: https://www.brit.co/sweet-beet-recipes/
Fudgy vegan beet cupcakes recipes: https://minimalistbaker.com/fudgy-vegan-beet-cupcakes/
Raw Vegan recipes: http://rawfoodrecipes.com/ingredient/beet/
Beet soups: https://www.allrecipes.com/recipe/89057/beet-soup/
21 beet dessert recipes: https://www.brit.co/sweet-beet-recipes/
Fudgy vegan beet cupcakes recipes: https://minimalistbaker.com/fudgy-vegan-beet-cupcakes/
Side effects when eaten in excess:
Beets, if eaten in excess, may cause the following problems:
- Beeturia: They can cause your urine to turn pink. While this is not a health problem, it is important to note the pink urine from beets as an indication that you may be deficient in iron.
- Kidney stones: Beets contain oxalates, which when consumed in excess can cause kidney and bladder stones.
- Allergy: Some people develop rashes, hives, itchiness, or even chills when they eat beets.
- Colored stools: Beets can cause the stools to appear pink or red in color due to its natural pigments. This is harmless, but if it continues for a few days, you may want to avoid beets to stay safe.
- Low blood pressure: Due to its ability to lower blood pressure, people on blood pressure medications should exercise caution when eating beets to avoid health complications.
- Blood sugar spike: Beets are high in sugar and also moderately high in the glycemic index list. Excess intake can cause a sudden spike in blood sugar levels. Speak with your doctor about consuming them if you are diabetic.
- Pregnancy: Pregnant women should avoid excessive consumption of beets due to the high levels of nitrates, as they may be sensitive to it.
- Flatulence: Eating too many beets can cause indigestion, stomach upset, loose stools, and flatulence due to high-fiber content.
- Gout: They are high in oxalates which can build up uric acid in the body, leading to gout.
Sources:
www.healthline.com
www.organicfacts.net
www.organicfacts.net